How does the AAV ELISA work?
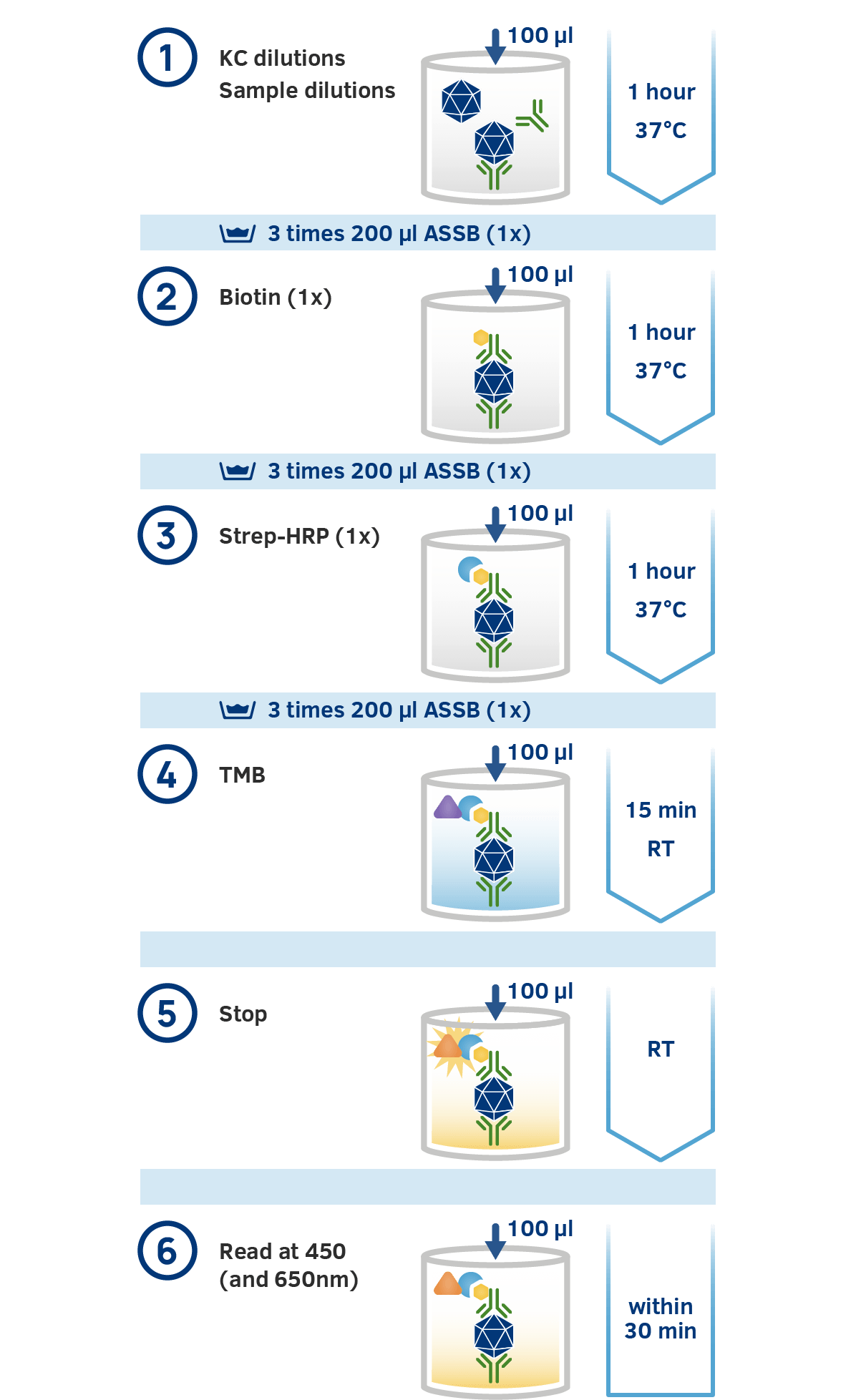
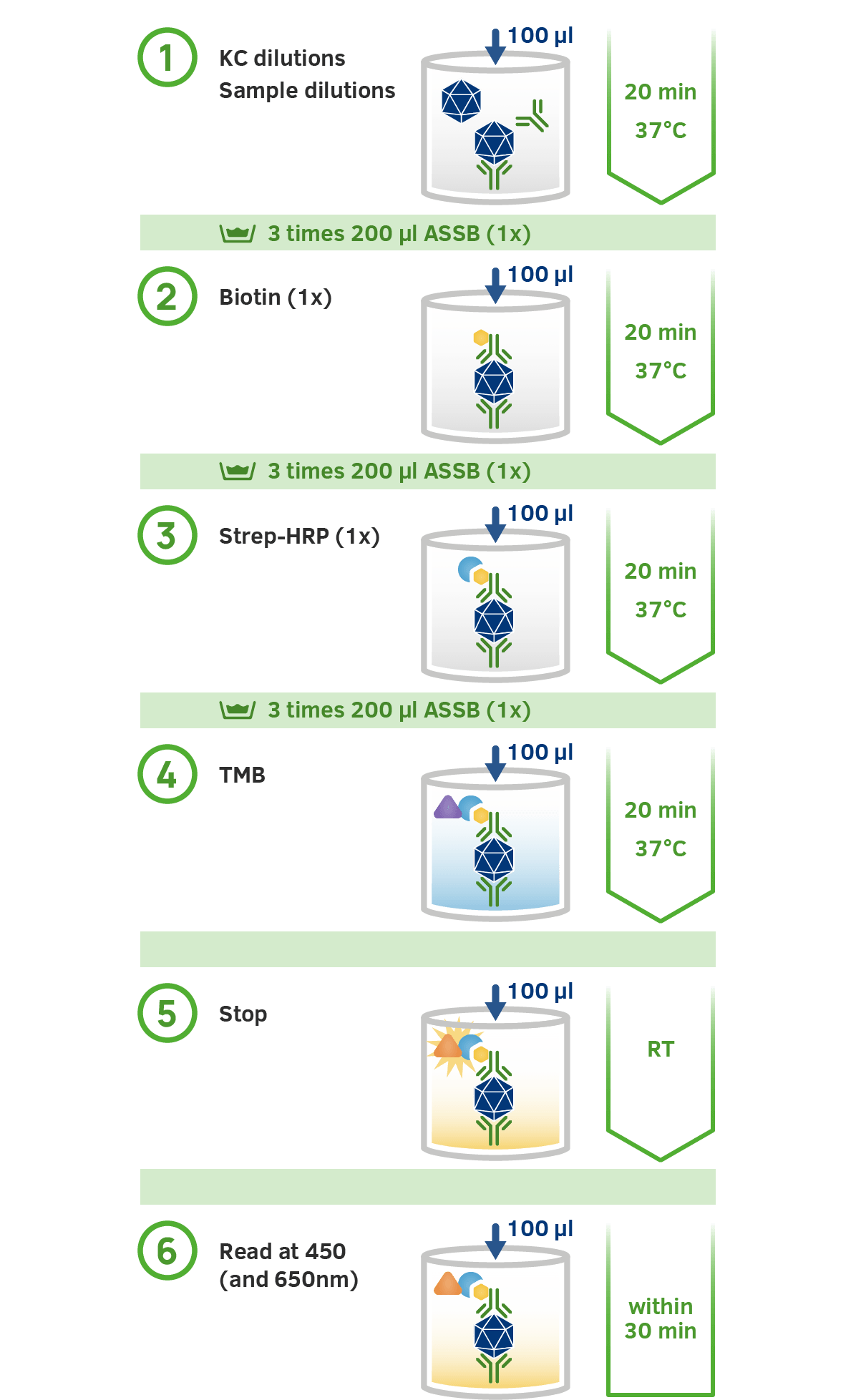
The assay is based on the sandwich ELISA technique. A monoclonal antibody specific for a conformational epitope on assembled AAV capsids is coated onto a microtiter plate to capture fully assembled AAV particles from the specimen.
Captured AAV particles are detected in a two step process.
-
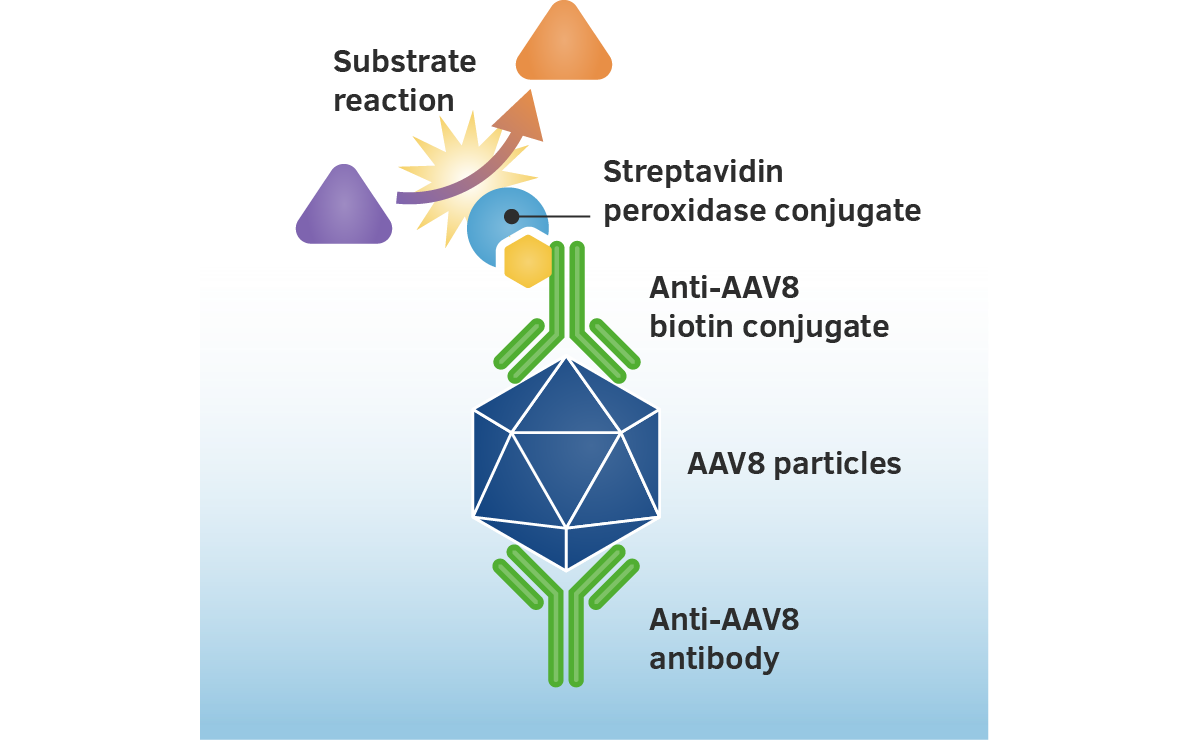
A biotin-conjugated monoclonal AAV antibody is bound to the captured AAV particles.
-
The streptavidin peroxidase conjugate reacts with the biotin molecules. After adding the substrate, the streptavidin conjugated peroxidase catalyses the substrate reaction producing a bright colour. The absorbance is measured photometrically at 450nm and is relative to the number of specifically bound viral particles.
Can your variant be detected by PROGEN antibodies?
The capture and detection antibodies used in PROGEN's AAV ELISAs specifically bind to defined conformational epitopes. These epitopes are only present on the surface of fully assembled capsids of the corresponding AAV serotypes. Changes in the protein sequences of the capsid proteins, e.g. in shuffled vectors, could influence the conformation of the proteins within the assembled particle, this in turn could interfere with the correct formation of the antibody binding epitopes found on the AAV capsid. Changes in the binding epitope alter the binding affinity of the antibody and affect the capsid titer determination based on the (non-shuffled) Kit Control provided with the AAV ELISA kit.
A first indication that the ELISA might recognize your shuffled AAV vector is the presence of the antibody-binding epitope. You can find more information about antibody binding sites of PROGEN's AAV antibodies in the FAQ section 'Do PROGEN AAV ELISAs recognize AAV shuffled vectors?.'
AAV ELISA Controls
Reliable positive controls in detections and quantification assays.